
What is Digital Transformation?
- Digital transformation is a business transformation first, encompassing the operating model, people, culture, and process.
- Digital transformation is a foundational and invasive endeavor, and it is not just putting some lipstick on a pig.
- Real digital transformation involves answering strategic questions such as, “What will my business look like at the end of this journey,” “What is our value-add and justification for existence,” “What do we make, sell, and how to make money.” These are existential questions and are not always black and white. For example, what a company makes/creates and how it makes its money may be very different in the digital age.
- Digital transformation is more than technology transformation. Technology is just an enabler.
- Customer-centric culture, strong leadership, and the ability to initiate and manage change are critical success factors in digitalization.
The key benefits of Digital Transformation are: Reduction in costs, Reduce parallel activities, Reduce damage to activities and impact the organization's operations, High-quality information, Faster and more efficient access to information, Proper implementation of organizational processes
Why Digital Transformation is a Need for your Business?
Most organizations today, even nonprofits and small companies, face the following challenges:
- Stakeholder demand for high efficiency and transparency
- Inspection agencies and regulators have become unpredictable
- Logarithmic growth of relationships with third parties and related risks
- High cost of identifying risks and meeting the requirements of upstream organizations
To meet these challenges, organizations create units and programs such as efficiency management programs, risk management programs, compliance programs and regulations, and public relations, but unfortunately, these programs and organizational units usually do not have the necessary impact and burden the organization which had the following consequences:
- High cost
- Lack of risk transparency
- Inability to determine the risks associated with working with third parties
- Impossibility to measure the effectiveness of managed risks
When these activities are overloaded, the likelihood of setting wrong and ineffective goals, unfavorable strategies, and ineffectiveness increases.
If you want to make a digital transformation journey to take advantage of the digital revolution, but do not know where to start, what standards to adopt, what are the costs, what are the benefits, what are the challenges, what are the opportunities, what are the strategies to follow, what are the right metrics to use, what are the technologies suitable for your business or activity, what is the percentage of success of this transformation and there are hundreds of more questions in your head,
Don't Worry
we are here to answer all these questions and help you to overcome the digital transformation challenges with a specific guideline for building your digital transformation strategy.
How we can help you
Succeeding on any trip requires careful planning. We have developed a model for a safe and secure journey into the digital world. In other words, we have made a plan for you, to make a journey, whose destination is the long-term success of your business, the travel space is the digital world, the means of travel is the governance of business and achieving its goals and fuel is information technology.
A digital transformation model is a compass for how to realize the digital transformation vision through a series of phases, activities, and milestones. The digital transformation model is a critical deliverable, and it should be more granular than a strategy document and a bit more abstract than a detailed project plan.
By using this model, you will have:
- Better customer experience
- Reduced cost of operations
- Better compliance
- Effective Risk Management
- More profound Customer Insights
- Data-driven Decision Making
- Elimination of reduction of Silos
- New Business Models, New Products, and Better Opportunities
- Employee empowerment
- More Collaboration
In this journey, we help you to securely go
From
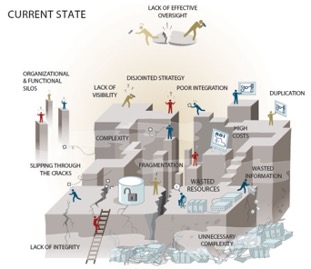
To
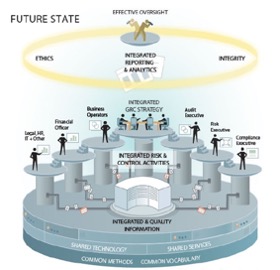
How our solution works
Our solution is based on framework and a model for implementation of that framework. The framework encompasses five major parts, which are:
To start any journey, you need to know where you are and to where you want to go. For this purpose, you need to know your business well. In a systematic approach, at first, mission, vision, goals and strategies should be defined.
Each organization is under effects of two environmental factors, which are external and internal.
External factors are:
- Political
- Economical
- Social
- Technical
- Environmental
- Legal
And, Internal factors are:
- Mission
- Vision
- Values
- Goals
- Strategy
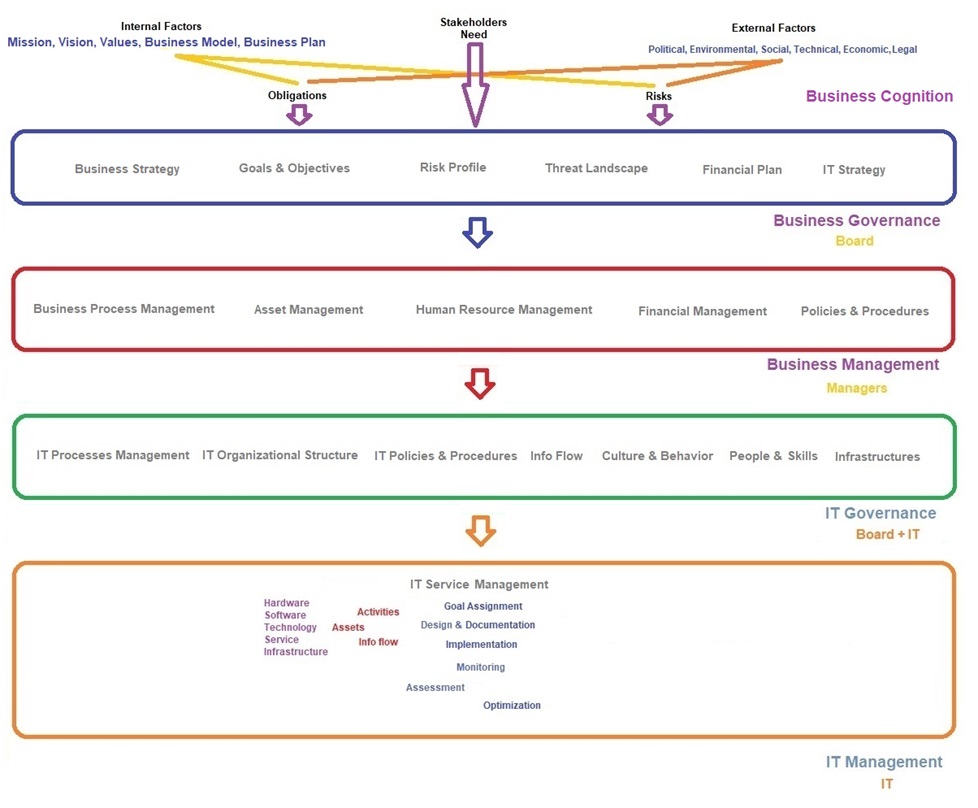
These factors impose risks and obligations on the organization and they should be managed by business governance. In other words, business governance concerns the actions and controls placed on those charged with managing a business entity. It is the collection of mechanisms, processes and relations used by various parties to control and to operate a business. Business governance generally concerns the internal control of a corporation as influenced or controlled by government law, rules of ethics, and industry standards. In addition to the above, the needs of stakeholders must also be considered. Board is responsible for business governance.
Business management is the administration of a commercial enterprise. It includes all aspects of overseeing and supervising business operations. From the point of view of management and leadership, it also covers fields that include office building administration, accounting, finance, designing, development, quality assurance, data analysis, sales, project management, IT management, research and development, and marketing.
According to Fayol, the five functions of management are:
- Planning
- Organizing
- Commanding
- Coordinating
- Controlling
As already, said, each business presents products and/or services and for this purpose, they should define some processes. To be able to run the processes, they need different types of assets such as hardware, software, human resource, buildings and also, they need procedures and information. Therefore, for business management, the followings should be identified, documented and improved:
- Processes
- People
- Technology
- Assets
If we consider that people and technology are assets embedded in processes to provide the required outputs., then if we manage and improve processes, we can manage business and achieve its goals. Therefore, Business Processes Management (BPM) is the most important activity in this phase.
Information technology is an important factor in achieving success in the information economy and central to an entity’s operational and financial management. As a result, enterprise governance and IT governance can no longer be considered separate and distinct disciplines. IT governance provides the structure that links IT processes, IT resources and information to enterprise strategies and objectives.
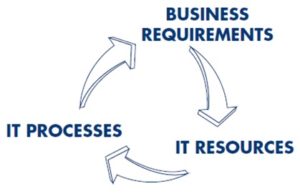
IT Management is the process of overseeing all matters related to information technology operations and resources within an IT organization. IT management ensures that all technology resources and associated employees are utilized properly and in a manner that provides value for the organization. The objective of IT management is to deliver value to the customer in the form of services. The key objective is to understand parameters and needs involved in a good service delivery. This is viewed from the service provider’s perspective, looking at the client or business.
At a basic level, IT governance provides the roadmap for what needs to be done, and IT management offers the means of achieving those ends. For instance, managers could use IT governance to decide what processes the organization needs, and IT management tells them how to carry them out. Additionally, IT governance handles the IT resource questions from the perspective of the business as a whole, while IT management approaches the issues strictly from the perspective of IT. IT governance takes the “from the top down” route, and IT management uses the “from the bottom up” path. IT governance describes what should be done in IT and IT management describes how to it. IT is prime focus of IT management and IT governance has enterprise perspective.
In this phase the following should be provided:
- Goal Assignment for IT Services
- Design & Documentation of IT Services
- Implementation of IT Services
- Monitoring of IT Services
- Assessment of IT Services
- Optimization of IT Services
How our solution works
And the model which is a compass for how to realize the digital transformation vision through a series of phases, activities, and milestones, is based on PPDIOO (Prepare, Plan, Design, Implement, Operate, and Optimize) model, which has six phases:
For any safe journey, you should know where you are and to where you want to go. Then you have to pack your luggage and prepare yourself. Organizations that wish to implement IT projects should put a few prerequisites in place right at the beginning, to ensure that the principles are adopted in the long term.
Business Cognition
- Business Model
- Business Plan
- Stakeholders
- Business Obligations
- Organizational Structure
- Products & Services
- Personnel
- Assets
- Business Processes
- Business Rules & Events
- IT Infrastructure
- IT Maturity Level
Business Governance
- Management Support
- Stakeholder’s Needs
- Business Strategy
- Business Goals & Objectives
- Risk Profile
- Threat Landscape
- IT Strategy
Business Management
- Required Resources
- Required Information
- Proper Level of Culture and Maturity
- Sufficient Skilled Manpower
- Manage Challenges
The purpose of the plan phase is to ensure a shared understanding of the vision, current status, and improvement direction for all project’s products and services across the organization. The plan activity covers strategic, tactical and operational direction and planning, it ensures requirements from the business are understood and validated and that the necessary polices are followed. A project plan is useful for helping manage the tasks, responsibilities, critical milestones, and resources required to implement digital transformation. The project plan should align with the scope, cost, and resource parameters established in the original business requirements.
Business Governance
- Engagement
- Roadmap
- Budgeting
- Digital Transformation strategy
Business Management
- Steering Team Setup
- Project Management
The design specification is the basis for the implementation activities. It is a comprehensive detailed design that meets current business and technical requirements, and incorporates specifications to support its availability, reliability, security, scalability, and performance.
Business Governance
- Manage Business Process
- Selection
- Analysis
- Goal Assignment
Business Management
- Determining the amount and role of Information Technology in the Business Processes
- Assess IT Maturity Level
- Redesign Business Processes with a view to increasing the level of IT Maturity
IT Governance
- Determine Information Technology Goals using Business Goals
- Prioritize IT Governance Processes based on IT Goals
- Provide the required Documents for IT Governance high priority processes in the following categories:
- Evaluate, Direct, Monitor
- Align, Plan, Organize
- Build, Acquire, Implement
- Deliver, Service, Support
- Monitor, Evaluate, Assess
IT Management
- Identify Information Technology Services
- Improve the level and efficiency of IT services in accordance with the set goals
- Develop a service strategy using EDM documents
- Plan and engage stakeholders using APO documents
- Provide IT Services Design documents using APO documents including:
- Service structure
- Architecture management
- Continual improvement
- Information security management
- Knowledge management
- Measurement and reporting
- Portfolio management
- Organizational change management
- Project management
- Relationship management
- Risk management
- Service financial management
- Strategy management
- Supplier management
- Workforce and talent management
- Availability management
- Business analysis
- Capacity and performance management
- Change enablement
- Incident management
- IT asset management
- Monitoring and event management
- Problem management
- Release management
- Service catalogue management
- Service configuration management
- Service continuity management
- Service design
- Service desk
- Service level management
- Service request management
- Service validation and testing
- Deployment management
- Infrastructure and platform management
- Software development and management
with considering
- Current situation
- Optimal situation
- Budget
- Responsible People
- Required Information
- Required Infrastructures & Technologies
- Suppliers and Customers
- Service Delivery Process
- Process Interfaces
So far, the IT services & processes are designed, now it is time to implement them. The purpose of this phase is to ensure that service components are available when and where they are needed and meet agreed specifications. This phase activities ensure that any components required for the delivery of services and products are either procured or built-in line with design specifications and service modelling.
The first thing should be done in this phase is Project Prioritization. In design phase many projects might be designed, but you have limited resource and may can’t implement all of them. Project prioritization is a process of management of the portfolio of IT projects. This process defines how IT projects are selected and also the priorities of IT projects.
- Project’s Prioritization
- Project’s Definition
- Projects Implementation
- Build or Buy IT Services using BAI documents and related design documents
- Implement IT Services using DSS documents and related design documents
The most user centric part of any ITSM service provider is delivery and support, it is here that services are made available for users to access. The purpose of this phase is to operate and deliver services and ensure that services are delivered and supported according to agreed specifications and stakeholders’ expectations. It is also where the service desk practice will be primarily focused given that they are the single point of contact for all support related to service issues (incidents) and requests. This phase activities are the most used and visible during daily use of services and products. Ultimately it is these activities which have the most direct link to the co-creation of value.
- Monitoring
- Monitor and support IT Services using DSS documents and related design documents
- Assessment & Audit
Optimization involves proactive management of the IT processes and services. The purpose of the optimization phase is to ensure continual improvement of products, service and practices. The goal of proactive management is to identify and resolve issues before they affect the organization.
An analysis of the current situation should precede any process reorganization; this will make it possible to decide which current processes may be left unchanged and where, on the other hand, there is an especially urgent need for action.
- Improvement
- Improve IT Services using MEA documents and related design documents
